The relentless, exponential growth of the Artificial Intelligence (AI) and High-Performance Computing (HPC) sectors has fundamentally and dramatically redefined the thermal challenges within the modern data center. The sheer power density of contemporary Graphics Processing Units (GPUs) and Central Processing Units (CPUs)—the specialized engines driving massive large language models and complex AI workloads—now frequently pushes power consumption past 700 Watts per chip.
This intense concentration of power creates localized heat densities that traditional air cooling systems can no longer manage reliably, efficiently, or economically. Attempting to cool these components with air leads to excessive energy consumption, higher PUE (Power Usage Effectiveness) values, and a high risk of component throttling or failure. This unprecedented thermal output necessitates a New Requirement for Advanced Heat Dissipation Technology in the AI Computing Power Era. To unlock the full potential and guarantee the continuous operation of high-density AI clusters, the industry must pivot to highly effective, liquid-based solutions.
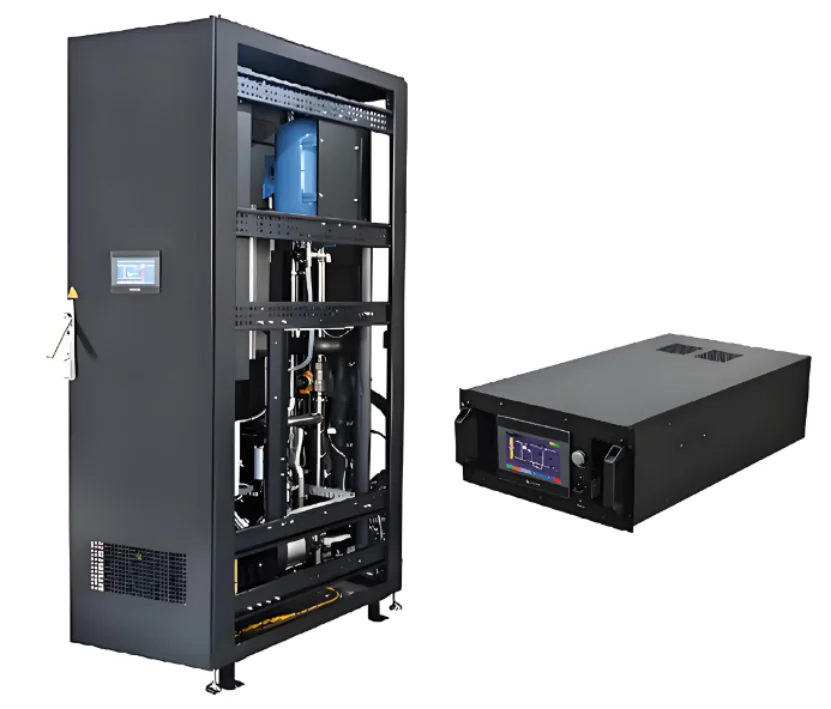
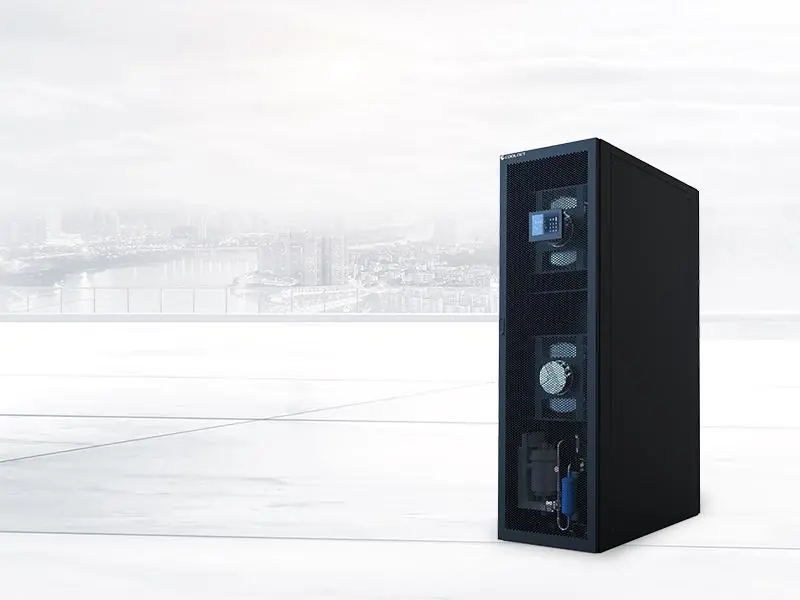
At Coolnet, we have proactively met this critical requirement by pioneering advanced liquid cooling specifically tailored for AI infrastructure. Our Cold Plate Liquid Cooling Solution provides the necessary thermal precision, efficiency, and exceptional scalability required for the world’s most demanding AI and HPC clusters. By moving the cooling medium directly to the heat source, we ensure maximum heat removal, enabling these cutting-edge chips to operate at peak performance without thermal constraints.
Technical Characteristics and Core Advantages of Liquid Cooling for AI
Liquid cooling for AI systems is far more than just an alternative to air cooling; it represents a necessary and fundamental thermal management shift for high-density environments. The advantage stems from the physics of heat transfer: liquid (typically a specialized water-glycol mixture or dielectric fluid) has a specific heat capacity thousands of times greater than air, making it vastly superior at absorbing and transferring heat.
Technical Characteristics:
Superior Heat Transfer Coefficient: Liquid provides highly efficient and uniform heat transfer directly away from the chip, minimizing dangerous temperature gradients across the semiconductor surface.
Extremely high power density support: Liquid cooling is currently the only proven and reliable method to handle the ever-increasing rack power density.
Reduced Auxiliary Energy Consumption: By capturing heat at the source, the need for high-speed, power-intensive server fans and large, inefficient Computer Room Air Conditioners (CRACs) is dramatically diminished, reducing acoustic pollution and significant auxiliary power draw.
Core Advantages:
The deployment of liquid cooling provides dual benefits: enhanced IT performance and significant infrastructure cost savings:
Elimination of Thermal Throttling: Maintaining chip temperatures well below critical thresholds is paramount. Liquid cooling guarantees this stability, preventing costly thermal throttling, which ensures CPUs and GPUs run at their highest boost clock speeds continuously for maximum computational throughput.
Dramatic PUE Reduction: The total energy consumed by the cooling system (pumps, CDUs, and external heat rejection) is significantly lower compared to air cooling infrastructure. This efficiency leads to a much lower overall Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE) for the facility, often pushing PUE figures toward the global benchmark of 1.2 or below.
Working Mechanism and Cooling Efficiency of Direct-to-Chip Liquid Cooling
Direct-to-chip liquid cooling is the most targeted and efficient approach, maximizing heat removal by circulating the coolant directly over the hottest components. Our Coolnet Cold Plate Liquid Cooling Solution utilizes this mechanism, centered around the crucial Coolant Distribution Unit (CDU).
Working Mechanism:
The process is a precise, sealed loop managed by the CDU:
Cold Plate Contact: Cold Plates—precision-engineered copper or aluminum blocks—are mounted directly onto the surface of the hot chips (GPUs, CPUs, FPGAs, and high-speed memory modules).
Heat Absorption: Chilled coolant, precisely regulated for temperature and flow by the CDU, flows through internal micro-channels within the cold plates, where it rapidly absorbs the intense heat generated by the silicon.
Heat Transport: The now-warm coolant travels out of the server via quick-disconnect couplings (QDCs) through a Rack Manifold to the CDU.
Heat Exchange: The CDU serves as the critical interface. It uses a plate heat exchanger to transfer the absorbed heat from the server-side fluid loop (the secondary loop) to the facility water loop (the primary loop). This two-loop architecture maintains a clean, sealed environment for the sensitive IT equipment while allowing the heat to be carried away for external rejection.
Cooling Efficiency:
This close-coupled mechanism offers unparalleled cooling efficiency because the heat is captured immediately at the source. It bypasses the highly inefficient steps of conventional cooling—heating air, which then heats a room, which must then be cooled by a PAC unit. This results in up to 80-90% of the total server heat being removed via the liquid loop, leaving minimal residual heat for the air cooling system to handle.
Application Value and Performance Improvement of Chip-Level Liquid Cooling in High-Density AI Clusters
The tangible Application Value of chip-level liquid cooling is realized most acutely within demanding High-Density AI Clusters, where every infrastructural gain yields exponential performance improvement.
Maximizing Rack Density: The phenomenal heat removal capacity of Direct-to-Chip Liquid Cooling allows for an unprecedented concentration of powerful chips within a single rack. This vastly increases the compute density (measured in TFLOPS per square foot) of the AI cluster, optimizing data center footprint utilization and reducing building costs.
Stable and Predictable Performance: AI training and inference require continuous, sustained processing power. By guaranteeing low, stable chip operating temperatures—often a full 10 Celsius to 20 Celsius cooler than air-cooled systems—the solution ensures reliable operation and eliminates the compute variability caused by temperature fluctuations.
Extended Equipment Lifespan and Reliability: Reducing the maximum operating temperature of semiconductors significantly mitigates long-term component degradation. Chip-level liquid cooling directly extends the service life of incredibly expensive AI accelerators (GPUs and TPUs), leading to substantial long-term savings in replacement costs and improving system reliability.
Integration with Sustainability Goals (Free Cooling): By allowing higher fluid temperatures in the primary facility cooling loop, liquid cooling systems are optimally compatible with free cooling technologies (using ambient air/water). This maximizes the annual hours spent using efficient free cooling, significantly bolstering a facility’s energy savings and sustainability profile.
Conclusion: Ensuring Stable and Efficient Operation of AI Systems through Precise Liquid Cooling Solutions
The exponential growth in AI computing power has firmly established liquid cooling for AI as a foundational requirement for next-generation data centers. Coolnet‘s direct-to-chip liquid cooling technology provides the necessary precision, efficiency, and scalability to manage the most extreme thermal loads generated by current and future AI clusters.
By implementing our advanced Cold Plate Liquid Cooling Solution, organizations can guarantee the stable and efficient operation of their critical AI systems, maximize their compute density, and achieve significant, measurable reductions in energy consumption, thereby securing a robust and future-proof thermal infrastructure.